Most organizations handle employee onboarding, multitasking, training, and setting up systems. However, the process that follows an employee's departure—known as offboarding—is just as, if not more important, especially in cybersecurity and compliance. Microsoft 365, a suite of productivity tools used by millions of businesses worldwide, is at the heart of many organizational operations. As such, ensuring that departing employees no longer have access to sensitive data, communications, and other resources within this platform is paramount.
Why is user offboarding important?
User offboarding is critical for Security. Errors in this process can result in accidental access to confidential information by former employees, resulting in potential data breaches, unauthorized disclosures, and compliance issues. Additionally, at a time when data breaches frequently make headlines and regulatory bodies are becoming increasingly strict, companies need to recognize the critical nature of offboarding.
By understanding the risks, using the right tools, and implementing best practices, organizations can protect their digital assets and reputations and ensure their ongoing safety and Security.
Understanding the Risks of Inadequate Offboarding
The process of offboarding employees is as critical as onboarding them. When not executed meticulously, inadequate offboarding can expose organizations to many risks. Let's delve into some of the most pressing concerns:
Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access
Employees have varying access to an organization's data depending on their role. If their access isn't revoked or modified appropriately upon departure, it leaves a gaping hole in the organization's security. Former employees can access sensitive information, intentionally or accidentally, leading to data breaches. Moreover, cybercriminals can exploit these vulnerabilities, accessing systems using old, unmonitored credentials.
Compliance Violations and Potential Legal Implications
Many industries operate under strict regulatory frameworks that mandate the protection of specific data types, like personal or financial information. Inadequate offboarding can result in non-compliance with these regulations. For instance, a former employee accessing personal data without authorization could violate regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Such violations lead to hefty fines and can result in legal actions against the organization.
Reputational Damage and Loss of Customer Trust
Trust is a cornerstone of customer loyalty. When news of data breaches or compliance violations becomes public, it can tarnish an organization's reputation. Customers and partners may question the organization's commitment to security and privacy. The aftermath of such incidents often sees a decline in customer trust, leading to loss of business, reduced revenue, and a long, uphill battle to rebuild the organization's image.
Organizations must recognize these risks and prioritize a comprehensive offboarding strategy to safeguard their assets, reputation, and future.
Critical Components of Microsoft 365 Offboarding
Ensuring this platform's secure and efficient offboarding process is essential as employees come and go.

Some of the critical components that make up a robust Microsoft 365 offboarding strategy are:
- User Account Management
Managing user accounts is the first and most obvious step in the offboarding process. When an employee departs, it's crucial to determine what to do with the account. Should it be disabled temporarily or deleted altogether? While some organizations prefer to deactivate accounts for a certain period to ensure a smooth transition, others may opt for immediate deletion to eliminate potential security risks. Regardless of the chosen approach, ensuring the departing employee can no longer access their account or any associated data is essential. This step also involves transferring critical files or emails to another team member and ensuring shared documents have a new owner.
- Data Retention and Archiving
Data is one of the most valuable assets for any organization. When an employee leaves, the data they've created, managed, or interacted with doesn't just disappear. It's vital to have a clear strategy for retaining and archiving this data. Microsoft 365 provides tools that enable organizations to establish data retention policies, preserving essential information for a specified period. It helps comply with various regulations and ensures organizations retain valuable knowledge. Furthermore, archiving ensures that while the data remains accessible for future reference, it doesn't clutter active storage or systems.
- License Management
Microsoft 365 operates on a licensing model, where users require a license to access various services. When offboarding, it's essential to reclaim and manage these licenses effectively. By doing so, organizations can ensure they're not paying for unused services and can reallocate licenses to new or existing employees as needed. Proper license management not only aids in cost-saving but also ensures that no unauthorized users continue to access services post-departure.
- Device and Application Access Control
In our modern work environment, employees often access Microsoft 365 services from multiple devices, be it laptops, smartphones, or tablets. Organizations must ensure they revoke access to these devices as part of the offboarding process. It involves removing company data from personal devices and ensuring that company-owned devices are reset or reassigned. Additionally, application access control is crucial. Departing employees might have had access to specific apps integral to their roles. Revoking this access ensures they can no longer interact with or manipulate organizational data or processes through these applications.
Offboarding within Microsoft 365 is not just about deactivating an email account. It's a multifaceted process that, when executed meticulously, ensures an organization's security, compliance, and operational efficiency. Understanding and implementing these critical components becomes paramount for businesses worldwide as the digital landscape evolves.
Best Practices for Microsoft 365 User Offboarding
Best Practices for Microsoft 365 User Offboarding are pivotal in ensuring that an organization's digital assets remain secure and that transitions happen smoothly.
One of the main steps in this process is the immediate revocation of access to critical systems. When an employee's departure is confirmed, organizations should terminate their access to essential platforms, applications, and databases within the Microsoft 365 suite. This immediate action minimizes the risk of unauthorized data access or potential breaches.
Alongside this, archiving user data and emails is crucial. By doing so, organizations can preserve essential communications and documents for future reference, ensuring they do not lose critical information in the shuffle.
Microsoft 365 serves as a collaborative platform where employees share files and folders. When offboarding, transferring shared asset ownership to another active user is essential. It ensures that projects remain uninterrupted and that there's clarity on who holds responsibility for specific data sets.
Equally important is removing the departing user from distribution lists and groups. If overlooked, sensitive internal communications could still be accessible to them, posing a potential security risk.

It's also imperative to revoke user licenses as part of an offboarding process, as it ensures that former employees can't access services and aids in cost-saving for the organization. These licenses can then be reallocated to new hires or existing employees, optimizing the organization's resources.
Enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA) becomes paramount. By implementing MFA, even if a departing employee still has login credentials, they would need a second verification form to access systems, adding an extra layer of security.
Within Microsoft 365, there are seven primary offboarding tasks to complete; they are:
1. Block Login & Microsoft 365 Access: Prevents former employees from accessing Microsoft 365 services.
2. Archive Employee's Mailbox: Retains crucial emails for successors or potential litigation.
3. Wipe Employee's Mobile Device: Ensure you remove business data from personal devices.
4. Redirect or Convert Employee's Email: Keeps the email address active, redirecting incoming emails to a successor.
5. Grant Access to OneDrive & Outlook Data: Retains access to important files and emails, especially if the account is only unlicensed and not deleted. Content is accessible 30 days post-deletion, but restoring the account extends this period.
6. Reassign or Delete Microsoft 365 License: Free up the license for other users or save costs. Retain email, contacts, and calendar data for 30 days after removing the license. You can access OneDrive content if you don't delete the account. PowerShell is a great way to perform this:
# Install the necessary module if not already installed
Install-Module -Name Microsoft.Graph -AllowClobber -Scope CurrentUser
# Authenticate with Microsoft Graph
Connect-MgGraph -Scopes
"User.Read.All",
"Directory.Read.All",
"User.ReadWrite.All"
# Fetch all users with the specific properties
$allUsers = Get-MgUser -Select "id,displayName,userPrincipalName,accountEnabled,assignedLicenses"
# Filter for disabled users with licenses assigned
$disabledUsersWithLicenses = $allUsers | Where-Object {
-not $_.AccountEnabled -and $_.AssignedLicenses.Count -gt 0
}
# Display the users
$disabledUsersWithLicenses |
Format-Table Id, DisplayName, UserPrincipalName, AssignedLicenses
# Remove licenses from the disabled users
foreach ($user in $disabledUsersWithLicenses) {
# Create a null license object to remove the license
$licenseRemoval = @{
"addLicenses" = @();
"removeLicenses" = ($user.AssignedLicenses | ForEach-Object { $_.SkuId })
}
# Update the user's license
Set-MgUserLicense -UserId $user.Id -BodyParameter $licenseRemoval
Write-Host "Removed licenses from $($user.DisplayName)"
}
# Disconnect from Microsoft Graph
Disconnect-MgGraph
7. Delete Employee's User Account: Cleans up the admin center and stops incoming emails to the deleted account.
The offboarding process could be more straightforward due to the complexity and number of services within Microsoft 365.
Microsoft 365 Tools for Offboarding
Microsoft 365 offers tools and features designed to streamline and secure the offboarding process. These tools ensure that departing employees are transitioned out of the system efficiently while protecting the organization's data. The main tools and features are:
- Azure Active Directory User Management
- Microsoft Security and Compliance Data Governance
- Microsoft Intune Device Management
- Identity Governance Lifecycle Workflows
Azure Active Directory User Management
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is pivotal in managing user identities and controlling resource access. During offboarding, it ensures that departing employees no longer have access to company resources, thereby safeguarding sensitive data and applications. Azure AD provides the following capabilities for user offboarding:
1. User Deletion/Deactivation: Immediately disable or delete a departing user's account to prevent unauthorized access.
2. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Ensure you revoke any elevated permissions granted to the user upon departure.
3. Audit Logs: Review logs to monitor any recent activity by the departing user and ensure no unauthorized actions occur.
Microsoft Security and Compliance Data Governance
This tool ensures that an organization's data complies with internal policies and regulations. During offboarding, it aids in retaining, archiving, or deleting user data based on these policies. Microsoft Security and Compliance provide the following capabilities for user offboarding:
1. Retention Policies: Determine policies for how long to retain a departing user's data before deleting it.
2. Data Archiving: Archive essential data from the departing employee for future reference or compliance needs.
3. Data Search: Locate and manage any sensitive or crucial data associated with the departing user.
Microsoft Intune Device Management
Intune ensures that company data on mobile devices is secure. Intune can remotely manage and wipe company data when employees leave, ensuring sensitive information doesn't leave. Microsoft Intune provides the following capabilities for user offboarding:
1. Remote Wipe: Remove company data from a departing employee's device without affecting personal data.
2. Complete Wipe: Completely reset a device's factory settings, erasing all data.
3. Device Compliance Policies: Ensure that devices adhere to company security standards and act if a non-compliant device is detected.
Identity Governance Lifecycle Workflows
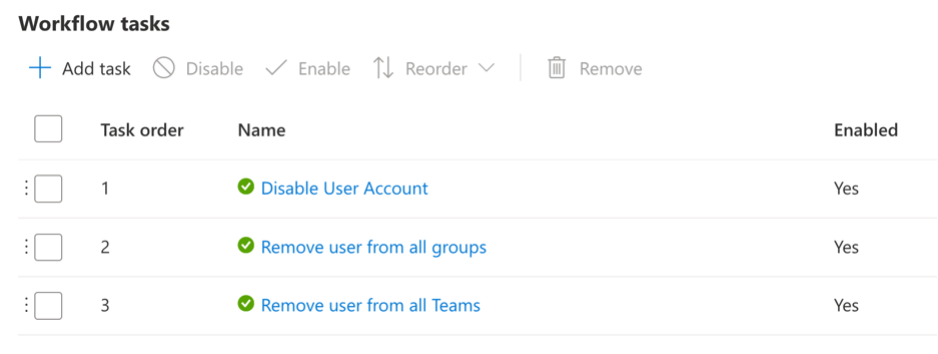
Identity Governance ensures that the right users have the proper access to resources. Combining Access Reviews, Entitlement Management, and Lifecycle Management controls the entire lifecycle of a provisioned user. Lifecycle workflows automate revoking access during offboarding, providing a consistent and thorough offboarding process. Identity Governance provides the following capabilities for user offboarding:
1. Access Reviews: Regularly review and certify user access, ensuring departing employees don't retain unnecessary permissions.
2. Entitlement Management: Manage access packages and policies and revoke any entitlements granted to the departing user.
3. Automated Workflows: Set up workflows to automate offboarding tasks, such as notifying relevant departments, revoking access, and archiving data.
Conclusion
Microsoft 365 provides some great tools, but many require extra licensing for all users. An example of this is Identity Governance which provides automated lifecycle workflows. Because of this, organizations do not utilize these tools. Another problem is that many features must approach consistency or work directly with each other, which means administrators implement PowerShell or other external processes. If you embrace all the capabilities and license all features within Microsoft 365, you will simplify the offboarding process; however, it targets only Microsoft 365 and Azure Services. However, you may need multiple services, administration centers, and PowerShell scripting.
Offboarding is a much larger process that often includes on-premises, cloud services, and applications. In this case, you need to look at a more holistic solution for offboarding, which could use the default capabilities specific to the applications and services you use.
Though Microsoft 365 services work well, many organizations must improve the notification process. For example, if an employee leaves, the department knows, and human resources know, but sometimes that is where it stops. IT and Security often don't know for quite a while later, exposing the organization due to the enabled account. Many organizations don't review or acknowledge security alerts, let alone anything else, such as offboarding. All departments and teams must work together to create an offboarding process.
Some other applications and services enhance the Microsoft 365 process for offboarding users. Specifically, the cloud collaboration governance SaaS Rencore Governance is one central tool to handle many cloud governance challenges, including user off boarding, by providing capabilities such as:
1. Instant overview of outstanding offboarding tasks: Rencore Governance provides an overview of all outstanding offboarding tasks in a single dashboard.
2. Pre-built policies: Rencore Governance offers pre-built customizable policies that continuously monitor and initiate the offboarding process.
3. Automated offboarding: Rencore Governance can automate the offboarding process, allowing IT admins to focus on other tasks.
4. Reporting: Rencore Governance provides detailed and dynamic reporting on the offboarding process.
5. Centralized management: Rencore Governance provides centralized management for the offboarding process.
Rencore Governance is simple to set up and use from the start. It’s a great tool that can help organizations automate and streamline the user offboarding process, saving time, money, and ensuring the secure and competent completion of offboarding.




